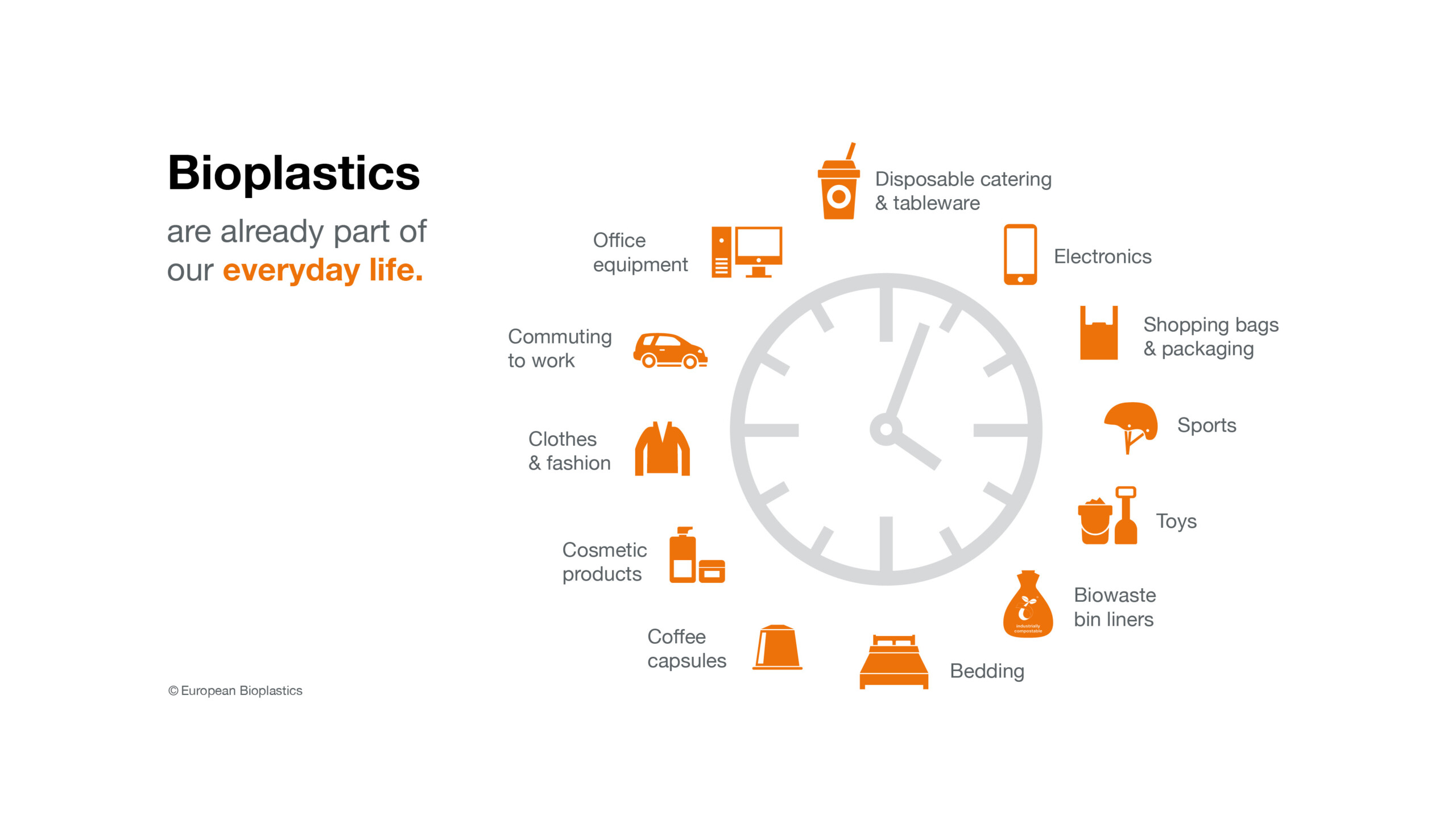
Applications for bioplastics
Today, bioplastics can be found in the following market segments:
- Packaging
- Food-services
- Agriculture & horticulture
- Consumer electronics
- Automotive & transport
- Consumer goods and household appliances
- Building & construction
- Coating & adhesives
- Fibers
Packaging
There is still a high demand for packaging made from bioplastics to be used for wrapping organic food as well as for premium and branded products with particular requirements. In 2023, global production capacities of bioplastics amounted to about 2.18 million tonnes with 43 percent (973,400 million tonnes) of the volume destined for the packaging market – the biggest market segment within the bioplastics industry.

Rigid bioplastics applications are available for cosmetics packaging of creams and lipsticks as well as beverage bottles and many more. Materials, such as PLA, bio-PE or bio-PET are used in this section. Several well-known brands, use bio-PET for bottles of all sizes containing drinks and other fluids, while Coca-Cola signed a cooperation to test the use of bottles made from PEF. Coca-Cola also introduced the “100 percent Plant-based Bottle” into the market. Procter & Gamble resorts to bio-PE to package some of its cosmetic products. As a potentially mechanically recyclable material, PLA is also gaining pace in the rigid packaging market.
Biodegradability is a feature often sought when it comes to food packaging for perishables. Flexible packaging solutions, such as films and trays are particularly suitable for fresh produce, such as fruit and vegetables, as they enable longer shelf life. The requirements for food packaging are as divers and numerous as there are different types of food. Today, packaging materials and processes are extremely sophisticated and easily adaptable to meet specific application and preservation needs. When it comes to protecting food and prolonging shelf life, the performance of bioplastics packaging is comparable to that of existing conventional packaging and sometimes even better. By continuing to improve barrier properties like antimicrobial coating and other aspects, the bioplastics industry will be able to achieve better preservation of food products than current packaging very soon.
For almost every conventional plastic material and application there is a bioplastic alternative available on the market that has the same properties and potentially offers additional advantages.

Food-services
Eating and drinking to go, takeaways and meal deliveries are part of modern lifestyle. According to Statista (2023), the revenue of the meal delivery market in Europe is projected to reach around 44.58 billion Euro in 2024 and is expected to grow to over 55 billion Euro by 2028. The European Commission’s political initiative for more sustainable solutions in the single-use segment, effective since July 2021, has initiated a process of re-defining the sector. Still, modern consumption asks for a mix of flexible single-use as well as reusable solutions because food hygiene and safety must continue to be ensured. In this context, a broad spectrum of bioplastics products is available for the food and catering segment. The selection ranges from cups, mugs, and trays to plates and cutlery – in single-use applications as well as reusable versions. There are numerous contexts where only single-use products provide viable solutions, especially in closed systems with an integrated waste management, e.g., on planes, at sport events, or in penal facilities.
Agriculture and horticulture
Biodegradable polymers offer specific advantages in agriculture and horticulture. Mulching films – the most important example – are generally making rapid advances in these sectors: production of pure foods with a minimum use of pesticide is a powerful sales argument in vegetable-growing or organic farming. Ploughing-in of mulching films after use instead of collecting them from the field, cleaning off the soil and returning them for recycling, is practical and improves the economics of the operation. Biodegradable mulching films today are very well adapted to the location and fruit.
Other promising applications in agriculture and horticulture include: films for banana bushes which have to be protected from dust and environmental influences, fastening technology, plant pots for propagation/cultivation, fertiliser rods, or pheromone traps, which no longer need to be removed after use.
Biodegradable plastics also offer opportunities for pot-plant marketing. Herb pots are a good example. Once the herbs are harvested, everything including the film can be composted. Alternatively, products can simply be planted into their pot, which is very convenient for hobby gardeners. Flower bulbs that can directly be planted into the soil in their packaging are also available. The packaging disperses quickly, and then plant growth can begin. The advantages of agricultural plastics are also clearly acknowledged by the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization.
Consumer electronics
A large proportion of consumer electrical appliances are made of plastics. Today, casings, circuit boards and data storage are made of plastic to ensure the appliances are light and mobile whilst being tough and, where necessary, durable. An increasing range of bioplastic products is introduced in the fast-moving consumer electronics sector: touch screen computer casings, loudspeakers, keyboard elements, mobile casings, vacuum cleaners, or a mouse for a laptop.
Automotive industry
In the automotive industry, manufacturers have turned to biobased or partly biobased durable bioplastics to produce sturdy dashboard components as well as solid interior and exterior features. Components made completely or partially from bioplastics can provide a standard of safety that is of ultimate importance in the transportation sector. The products include seat and airbag covers as well as steering wheels.
With new innovations on the way, bioplastics will take up a greater share of the composition of both automobiles and high-quality, fast-moving consumer electronics.